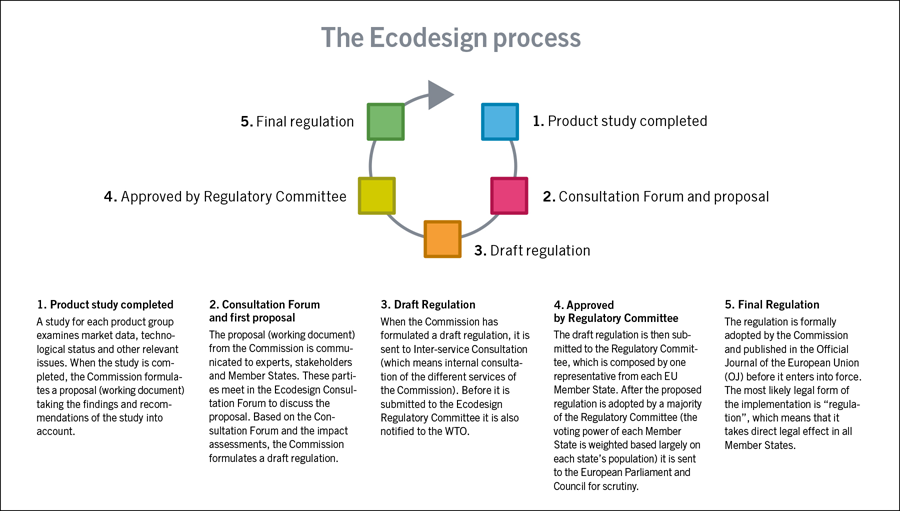
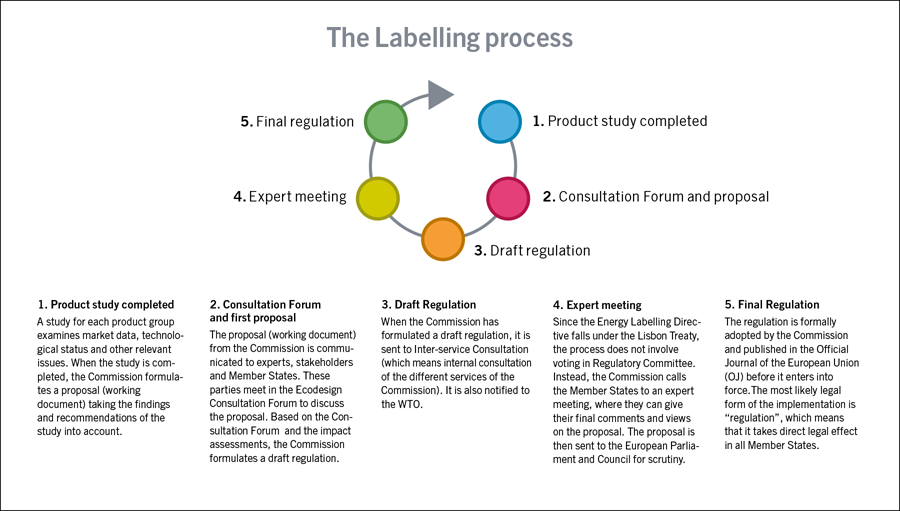
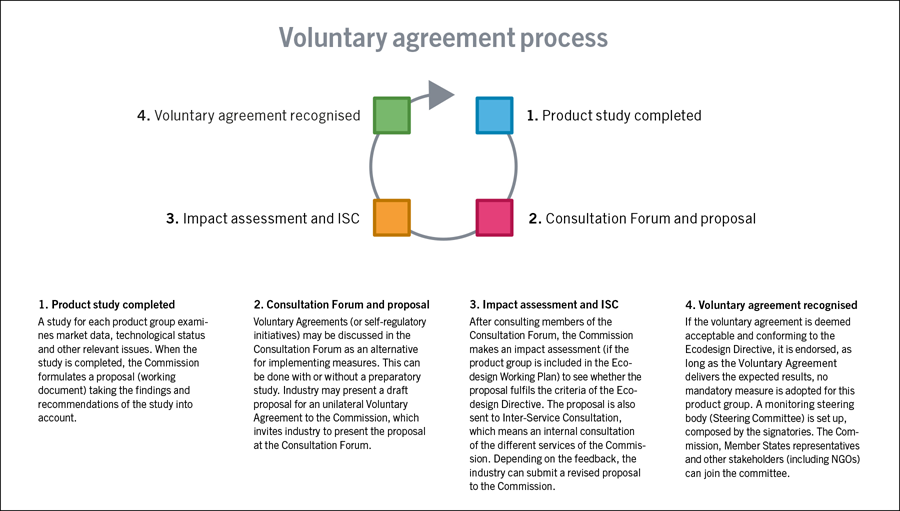
The energy labelling process
Labelling regulations are adopted as delegated acts. The process does not include voting in Regulatory Committee, as in the ecodesign process, but acts adopted by the Commission can be rejected by the Parliament and Council.
The procedure for adopting delegated acts differs from the adoption of Ecodesign regulations.The committee procedure is replaced by a new procedure in which the Regulatory Committee is omitted but stakeholders still discuss the proposals in Consultation Forum.
After Consultation Forum, the Commission adopts the delegated acts. However, they can still be rejected by the European Parliament or the Council within two months after the adoption.
The delegated acts are directly binding in all EU Member States after the entry into force.
Details in delegated acts
The delegated acts for energy labelling indicate the details related to the label and the fiche for each product. The label does not ban any product from the market. It gives consumers information to make the right purchasing decision. The aim is to to provide incentives to develop products beyond the mandatory energy efficiency levels.
The delegated acts indicate:
- a description of the product;
- measurement standards and methods;
- details of the technical documentation;
- the design and content of the label;
- the location where the label shall be fixed to the product;
- the duration of label classification.
View the energy labelling process in the flow chart in the right column.